تعلم قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة يمثل خطوة جوهرية لكل من يسعى إلى إتقان اللغة الإنجليزية وفهم بنيتها الزمنية بشكل دقيق. فالماضي البسيط هو الأداة التي تعبّرون بها عن أحداث وقعت وانتهت، سواء كانت مواقف يومية أو تجارب شخصية أو حتى وقائع تاريخية. من خلال هذا الزمن يمكنكم رواية القصص واسترجاع الذكريات بلغة صحيحة وواضحة.
كثير من المتعلمين يجدون أنفسهم في حيرة عند التعامل مع قاعدة الماضي البسيط، خصوصًا في التفرقة بين الأفعال المنتظمة وغير المنتظمة، أو عند تكوين النفي والسؤال بطريقة صحيحة.
ما هي قاعدة الماضي البسيط؟
قاعدة الماضي البسيط تُستخدم للتعبير عن الأفعال التي حدثت وانتهت في زمن محدد بالماضي. تُبنى الجملة عادة باتباع القاعدة: الفاعل + الفعل في التصريف الثاني (Past form) + بقية الجملة. هذا التصريف الثاني يختلف حسب ما إذا كان الفعل منتظمًا أو غير منتظمًا، فالأفعال المنتظمة تُضاف لها عادةً اللاحقة -ed في نهايتها، بينما للأفعال غير المنتظمة صيَغ خاصة يجب حفظها كما هي.
على سبيل المثال، تعبير He visited his grandmother yesterday يعني "زار جدته أمس"، ويُستخدم كثيرًا عند شرح قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة لأنه يُظهر بوضوح أن الحدث تم وانتهى في الماضي. وغالبًا ما يترافق زمن الماضي البسيط مع كلمات تدل على الوقت مثل yesterday أو last week أو in 2010 لتوضيح زمن وقوع الحدث بدقة.
ما استخدامات الماضي البسيط؟
يُستخدم زمن الماضي البسيط في عدة سياقات واضحة تتعلق بالماضي، من أبرزها:
- للحديث عن حدث منتهٍ: يُستخدم لوصف فعل وقع وانتهى في وقت محدد، مثل: She finished her homework last night.
- لسرد القصص أو الأحداث التاريخية: يساعد على عرض الأحداث بترتيبها الزمني، مما يجعل القصة واضحة وسلسة.
- لوصف تجارب سابقة: يُستخدم للتحدث عن شيء جرى في الماضي دون أن يستمر للحاضر، مثل: I traveled to Paris in 2018.
- لتوضيح العادات الماضية: يشير إلى سلوك أو عادة كانت تحدث بشكل متكرر ثم توقفت، مثل: They played football every weekend.
- لبيان تسلسل زمني بسيط: يشرح توالي الأحداث واحدة تلو الأخرى في زمن ماضٍ واضح ومحدد.
من خلال قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة، يمكنكم التعبير بدقة عن الأفعال الماضية وربطها بزمنها بطريقة صحيحة وسلسة في اللغة الإنجليزية.
كيف نكوّن جمل الماضي البسيط؟
في جمل الإثبات، تتكوّن قاعدة الماضي البسيط من: فاعل + الفعل في التصريف الثاني + مكملات الجملة. ويُستخدم التصريف الثاني سواء كان الفعل منتظمًا أو غير منتظم، حيث نضيف للفعل المنتظم (–ed) في نهايته، بينما الأفعال غير المنتظمة لها أشكال خاصة يجب حفظها كما هي، وهذا ما يظهر بوضوح عند دراسة قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة التي توضّح كيفية تطبيق كل نوع داخل الجملة
مثال: I walked to school yesterday.
كيف نصوغ النفي؟
لصياغة النفي في الماضي البسيط، نستخدم did not (أو الشكل المختصر didn’t) متبوعة بالفعل في صورته الأصلية (المصدر) دون أي إضافات، لأن الفعل المساعد did يحمل دلالة الزمن الماضي.
مثال: She didn’t eat breakfast this morning.
كيفية طرح الأسئلة؟
لطرح الأسئلة في زمن الماضي البسيط، نضع Did في بداية الجملة، ثم يأتي بعدها الفاعل، ثم الفعل في المصدر دون تصريف ثانٍ. تُستخدم هذه البنية مع جميع الأفعال بغضّ النظر عن نوعها، منتظمة كانت أم غير منتظمة.
مثال: Did you travel last summer?
ما الفرق بين الأفعال المنتظمة وغير المنتظمة؟
الأفعال المنتظمة في قاعدة الماضي البسيط تُصاغ بإضافة -ed إلى نهاية الفعل الأساسي، وهي الطريقة الأكثر شيوعًا لتكوين الماضي في اللغة الإنجليزية. ومع ذلك، توجد بعض القواعد البسيطة التي يجب الانتباه إليها وفقًا لنهاية الكلمة الأصلية:
- إذا انتهى الفعل بحرف e، نضيف فقط d.
- إذا انتهى بحرف y مسبوق بحرف ساكن، نُحوّل y إلى ied.
- إذا كان الحرف الأخير ساكنًا وقبله حرف متحرك قصير، نُضاعف الحرف الأخير قبل إضافة ed.
- play → played
تم إضافة ed ببساطة. - watch → watched
تم إضافة ed ببساطة. - study → studied
انتهى الفعل بـ y بعد حرف ساكن، لذلك تحولت y → i ثم أضيفت ed. - love → loved
ينتهي الفعل بحرف e، لذا نضيف d فقط. - stop → stopped
الفعل قصير وينتهي بحرف ساكن بعد حرف متحرك، لذلك تم تضعيف الحرف الأخير ثم إضافة ed.
ما هي الأفعال غير المنتظمة؟
الأفعال غير المنتظمة لا تتبع قاعدة محددة عند تحويلها إلى الماضي البسيط، إذ يتغير شكلها تمامًا، لذا من الضروري حفظها كما هي.
من أشهر الأمثلة على الأفعال غير المنتظمة:
- go → went
- eat → ate
- have → had
- do → did
- come → came
كيف أميز بينهما؟
التمييز بين الأفعال المنتظمة وغير المنتظمة يعتمد على معرفة القوائم الخاصة بالأفعال الشاذة (Irregular Verbs). فإذا كان الفعل واردًا ضمن هذه القوائم، فهو غير منتظم. أما الأفعال الأخرى التي يمكن أن نكوّن ماضيها بإضافة -ed فهي غالبًا منتظمة.
من المهم تدريب أنفسكم على حفظ أكثر الأفعال غير المنتظمة شيوعًا لأن إتقانها يساعد بشكل كبير في تطبيق قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة بطريقة صحيحة وسليمة في الممارسة اليومية للغة.
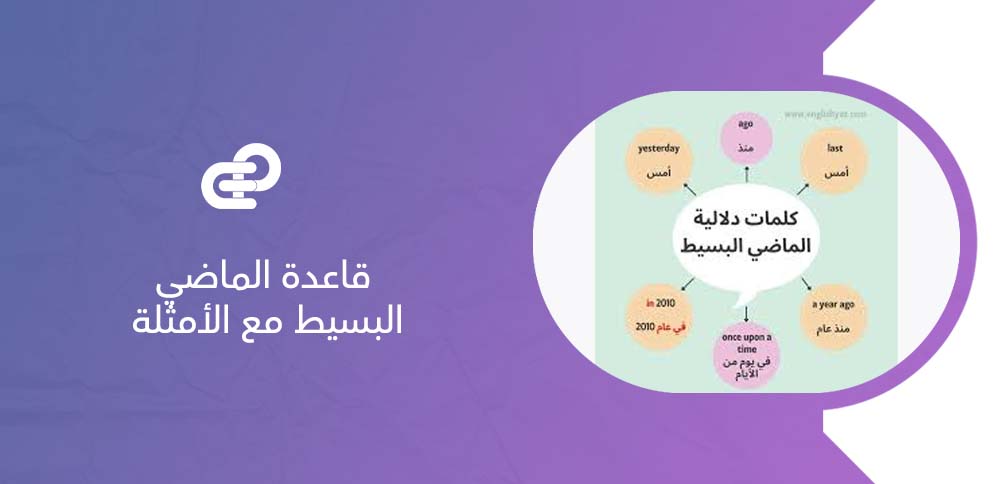
ما هي الكلمات الدالة على الماضي البسيط؟
تُستخدم كلمات محددة في اللغة الإنجليزية لتوضيح أن الجملة تتبع قاعدة الماضي البسيط، إذ تُشير هذه الكلمات إلى أن الحدث وقع وانتهى في زمن سابق. وجودها في الجملة يساعد على فهم سياق الزمن المقصود بسهولة.
- yesterday (أمس): تُستخدم للإشارة إلى حدث حدث في اليوم السابق مباشرة، مثل أن نقول إن شخصًا قام بفعل محدد بالأمس.
- last مثل: last week أو last year: تُعبّر عن فترة زمنية ماضية محددة انتهت بالفعل، مثل الأسبوع الماضي أو العام الماضي.
- ago مثل: two days ago: تُستخدم لتحديد المدة الزمنية التي تفصل بين الحدث والوقت الحالي، وتشير بوضوح إلى زمن منتهٍ.
- in مع السنوات أو أوقات محددة مثل: in 2020: تُوظف لتحديد العام أو الفترة التي وقع فيها الحدث سابقًا.
- once: تُفيد حدوث الفعل مرة واحدة في الماضي، وغالبًا تُستخدم عند سرد التجارب أو الذكريات.
- when: تأتي لربط حدثين وقعا في الماضي، حيث تُستخدم لتحديد اللحظة التي وقع فيها الفعل.
- the other day: تشير إلى وقت قريب مضى، وتُستخدم عندما لا تكون هناك حاجة لتحديد اليوم بدقة.
كيف أستخدم الماضي البسيط في مواقف الحياة اليومية؟
استخدام قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة في الحوار اليومي يجعل اللغة أكثر طبيعية وسلاسة. يمكن توظيفها في جمل الإثبات أو النفي أو السؤال للتحدث عن أحداث وقعت في الماضي:
- I visited my friend yesterday. زرت صديقي أمس.
- I didn’t watch TV last night. لم أشاهد التلفاز البارحة.
- Did you see John yesterday? هل رأيتم جون أمس؟
تنويع الجمل بين هذه الأشكال يساعدكم على فهم القاعدة أكثر ويُسهم في استخدامها بشكل تلقائي أثناء الحديث.
أمثلة في الكتابة والسرد
عند كتابة القصص أو تدوين المذكرات، يُعتبر الماضي البسيط الزمن الأنسب لسرد الأحداث التي انتهت بالفعل. فهو يمنح النص إحساسًا بالترتيب الزمني والتتابع المنطقي للأحداث. على سبيل المثال:
Last summer, I traveled to Spain with my family. We visited many museums and tried new food.
سافرنا الصيف الماضي إلى إسبانيا مع العائلة، وزرنا العديد من المتاحف وجربنا أطعمة جديدة.
هذا النمط في الكتابة يجعل القارئ يتتبع الأحداث بسهولة وكأنها مشهد حيّ من الذاكرة.
كيف أصف العادات القديمة؟
يمكن استخدام الماضي البسيط أيضًا للتحدث عن العادات التي كنتم تقومون بها في الماضي ولم تعودوا تمارسونها الآن. مثلًا:
When I was a child, I always played in the park after school.
عندما كنت طفلًا، كنت ألعب دائمًا في الحديقة بعد المدرسة.
هذا الاستخدام يُظهر بوضوح الفرق بين الماضي والحاضر، ويُساعد في التعبير عن الذكريات والعادات القديمة بطريقة بسيطة وواضحة.
ما الأخطاء الشائعة في استخدام الماضي البسيط؟
من أكثر الأخطاء شيوعًا بين المتعلمين إضافة اللاحقة –ed إلى جميع الأفعال، بما في ذلك الأفعال غير المنتظمة. يؤدّي هذا إلى تكوين كلمات غير صحيحة مثل: eated بدلًا من ate أو goed بدلًا من went. ويظهر هذا الخطأ كثيرًا عند دراسة قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة، حيث يتضح أن فهم قائمة الأفعال الشاذة والتدرّب على حفظها يساعدكم على استخدام صيغة الماضي البسيط بدقة أكبر عند بناء الجمل.
خطأ استخدام الفعل الماضي مع did/didn’t
يخطئ بعض المتعلمين باستخدام صيغة الماضي بعد الفعل did في الأسئلة أو النفي، رغم أن did نفسها تعبّر عن الماضي. في هذه الحالة يجب أن يأتي الفعل بعدها بصيغته الأساسية لا الماضية.
- الجملة الخاطئة: Did you went to the park?
- الجملة الصحيحة: Did you go to the park?
- الجملة الخاطئة: You didn’t watched the movie.
- الجملة الصحيحة: You didn’t watch the movie.
التمييز بين الدور النحوي لـ did والفعل الرئيسي أساسي لتجنّب هذه الأخطاء المتكررة.
نسيان الكلمات الدالة
الكلمات الدالة مثل yesterday، last week، أو two days ago ضرورية لتحديد زمن الحدث بدقة. نسيانها يجعل معنى الجملة غامضًا وقد يُفهم على أنه زمن آخر.
على سبيل المثال:
- I visited my friend. (قد تبدو عامة وغير محددة)
- I visited my friend yesterday. (توضّح أن الزيارة حدثت في الماضي القريب بوضوح)
اختلاط الأزمنة
يحدث أحيانًا أن يخلط المتعلمون بين الماضي البسيط وأزمنة أخرى مثل present perfect أو الحاضر البسيط، مما يغيّر معنى الجملة بالكامل. استخدام الماضي البسيط يعبّر عن حدث انتهى في وقت محدد، في حين أن الأزمنة الأخرى تشير إلى استمرارية أو ارتباط بالحاضر. التدريب على التمييز بين هذه الحالات يضمن لكم إتقان قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة الصحيحة.
كيف تطبّق أكاديمية انقلش بليس قاعدة الماضي البسيط؟
تقدّم أكاديمية انقلش بليس دروسًا مباشرة يتفاعل فيها المتعلمون مع المدرسين بطريقة عملية. خلال الحصص، يشارك الجميع في محادثات وتمارين فورية لتطبيق قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة بشكل حي، مما يساعدهم على فهم القاعدة واستخدامها بطلاقة في المواقف اليومية.
تمارين وأمثلة واقعية
يعتمد المدرسون على مجموعة من التمارين مثل إكمال الجمل وتصحيح الأخطاء واختيار الفعل الصحيح بصيغة الماضي. يتم تعزيز الفهم باستخدام أمثلة واقعية من الحياة اليومية كي يربط المتعلم بين اللغة والمواقف الحقيقية، مثل الجملة:
I played football yesterday.
بهذه الطريقة، يتدرّب الطلاب على استخدام القاعدة في سياقات مفهومة وواضحة بدلًا من الحفظ المجرد.
التدرج في الشرح وتبسيطه
تتبع الأكاديمية نظامًا تدريجيًا يبدأ من الأساسيات حتى يصل إلى الاستخدام المتقدم. كل وحدة تركز على نوع محدد من الجمل مثل الإثبات أو النفي أو السؤال، بالإضافة إلى التفريق بين الأفعال المنتظمة وغير المنتظمة. يتم تكرار ومراجعة القاعدة باستمرار لضمان ترسيخها دون تعقيد.
الأسئلة الشائعة حول قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة
ما هي قاعدة زمن الماضي البسيط؟
قاعدة زمن الماضي البسيط تُستخدم للتعبير عن حدث انتهى في زمن محدد في الماضي. تُبنى الجملة عادة من الفاعل + الفعل في التصريف الثاني، ويُستخدم هذا الزمن سواءً للحديث عن أحداث قصيرة أو طويلة المدى ما دامت قد انتهت بالفعل.
ما هي الكلمات الدالة الأهم؟
الكلمات الدالة على زمن الماضي البسيط تساعد في تحديد الإطار الزمني للجملة، ومن أهمها: yesterday، last (مثل last week أو last year)، ago، in + السنة مثل in 2022، بالإضافة إلى once وwhen.
هل تختلف القاعدة بين الحديث والكتابة؟
القاعدة واحدة في الشكل بين الحديث والكتابة، لكن الاختلاف يظهر في الأسلوب. ففي الكتابة يُراعى التسلسل الزمني بدقة ويُستخدم ربط الجمل بالعبارات الزمنية المناسبة، بينما في الحديث تُستخدم الجمل بصورة أبسط وأقصر.
الخلاصة
إتقان قاعدة الماضي البسيط مع الأمثلة يُعد خطوة جوهرية لكل من يسعى لإتقان اللغة الإنجليزية، لأنه يمنح المتعلم القدرة على التعبير بدقة وسلاسة عن الأحداث التي عاشها أو تعلمها في الماضي. فهم استخدام الفعل بشكل صحيح في هذا الزمن هو أساس للتواصل الفعّال في مختلف المواقف اليومية والتعليمية.
مقالات ذات صلة:

تعليقات:
لا يوجد تعليقات
[[c.user.fullname]]
[[reply.user.fullname]]