هل صادفتم من قبل صعوبة في فهم قاعدة الماضي التام في اللغة الإنجليزية؟ كثير من المتعلمين يواجهون التباسًا بينها وبين الأزمنة الأخرى مثل الماضي البسيط والماضي المستمر، رغم أن إتقانها يُحدث فرقًا واضحًا في جودة الكتابة والتحدث. هذا المقال مخصص لمساعدتكم على تجاوز تلك العقبة، واكتساب فهم دقيق لتركيب جمل الماضي التام وكيفية استخدامه في مواقف متعددة.
ستكتشفون خلال القراءة كل ما تحتاجونه لتطبيق قاعدة الماضي التام بسهولة: من شرح الاستخدامات والبنية اللغوية، إلى المقارنة مع الأزمنة الأخرى، مرورًا بتدريبات عملية وأمثلة توضيحية. المقال يناسب جميع المستويات، سواء كنتم في البداية وتبحثون عن أساس قوي في الأزمنة، أو متقدمين ترغبون في تحسين دقتكم اللغوية.
ما هي قاعدة الماضي التام؟
زمن الماضي التام هو أحد الأزمنة في اللغة الإنجليزية يُستخدم للتعبير عن حدث وقع قبل حدث آخر في الماضي. يوضح هذا الزمن الترتيب الزمني بين حدثين، بحيث يشير الحدث المصاغ بالماضي التام إلى الفعل الأسبق، بينما يُعبّر الحدث الآخر بصيغة الماضي البسيط. يساعد هذا الزمن في سرد الأحداث بوضوح ومنع الالتباس في تسلسلها.
ما تركيب قاعدة الماضي التام؟
يتكون تركيب قاعدة الماضي التام من عناصر محددة وواضحة، هي:
- الفاعل (Subject) +
- had +
- التصريف الثالث للفعل (Past Participle)
أمثلة:
- She had finished her homework before he arrived.
- I had seen the movie before she told me about it.
متى نستخدم الماضي التام؟
يُستخدم الماضي التام عندما نرغب في وصف حدثين حدثا في الماضي، ونحتاج إلى توضيح أيهما وقع أولاً. فعلى سبيل المثال، إذا انتهى أحد الأشخاص من عمل ما قبل وقوع حدث آخر، فإننا نُعبّر عن الحدث الأول بالماضي التام لبيان الأسبقية.
كما يُستعمل هذا الزمن لتوضيح ترتيب الأحداث في الحالات التي قد لا يكون فيها التسلسل الزمني واضحاً من السياق. فهو يُبرز الحدث الأسبق ويمنح الجملة وضوحاً أكبر، خصوصاً في السرد أو عند مقارنة أفعال متعددة جرت في أوقات متقاربة في الماضي.
كيف نصيغ جملة في الماضي التام؟
ما تركيب الجملة المثبتة؟
يُستخدم زمن الماضي التام عندما نريد التعبير عن حدث وقع قبل حدث آخر في الماضي. ويكون تركيب الجملة المثبتة كالآتي:
Subject + had + التصريف الثالث للفعل.
مثال: They had already eaten when I arrived.
تُظهر هذه الجملة أن الأكل حدث أولًا (باستخدام الماضي التام)، ثم تلاه حدث الوصول (في الماضي البسيط). هذا الترتيب يُبرز العلاقة الزمنية بين الحدثين بوضوح.
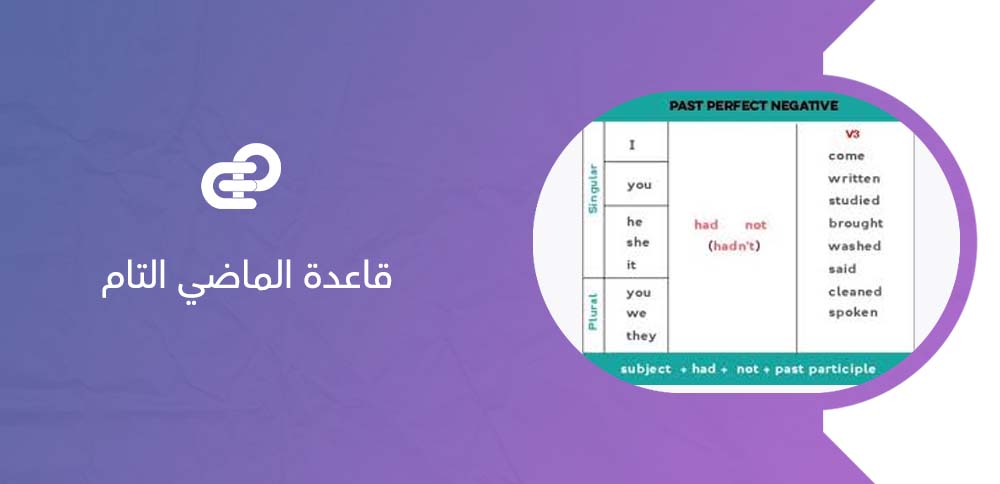
كيف نصوغ النفي؟
لصياغة النفي في الماضي التام نضيف كلمة not بعد "had"، فيصبح التركيب:
Subject + had not + التصريف الثالث للفعل.
مثال: I had not seen that film before yesterday.
نلاحظ هنا أن النفي يشير إلى أن الفعل (رؤية الفيلم) لم يكن قد تحقق قبل نقطة زمنية معينة في الماضي. يُستخدم هذا الشكل لتوضيح أن الحدث لم يكتمل أو لم يقع قبل حدث آخر.
كيف نكتب سؤال بالماضي التام؟
عند تكوين سؤال في زمن الماضي التام نبدأ بالفعل Had قبل الفاعل، ثم نضيف التصريف الثالث للفعل. أي أن التركيب يكون:
Had + Subject + التصريف الثالث للفعل.
مثال: Had you finished your homework before dinner?
ولتكوين هذا النوع من الأسئلة يمكن اتباع الخطوات التالية:
- ضع “Had” في بداية الجملة.
- أضف الفاعل مباشرةً بعدها.
- استخدم التصريف الثالث للفعل المراد التحدث عنه.
- أكمل الجملة لتحديد الحدث اللاحق في الماضي.
بهذا الترتيب، يساعد الماضي التام على توضيح الفعل الذي تم قبل غيره، مما يجعل تسلسل الأحداث في الماضي أكثر دقة ووضوحًا.
ما الفرق بين الماضي التام وباقي الأزمنة؟
يُستخدم الماضي التام عندما يقع حدث قبل حدث آخر في الزمن الماضي، أي أن أحد الفعلين يُعبّر عن حدث أسبق من الآخر. أما الماضي البسيط فيُستخدم لحدث واحد انتهى في الماضي دون الإشارة إلى ترتيب زمني مع حدث آخر.
على سبيل المثال:
- I had eaten تعني "كنت قد أكلت" وتشير إلى أنّ فعل الأكل حدث قبل حدث آخر في الماضي.
- I ate تعني "أكلت" وتدلّ فقط على وقوع الحدث في الماضي دون وجود حدث لاحق مرتبط به.
إنّ تمييز قاعدة الماضي التام عن الماضي البسيط يعتمد أساسًا على تسلسل الأحداث؛ فالحدث الأسبق يُعبّر عنه بالماضي التام، والحدث اللاحق أو المنفصل بالماضي البسيط.
ما الفرق مع الماضي المستمر؟
بينما يُستخدم الماضي التام للتعبير عن حدث انتهى قبل حدث آخر، فإن الماضي المستمر يصف حدثًا كان جاريًا في فترة محددة من الماضي، وغالبًا ما يُظهر أنّ حدثًا جديدًا قاطع ذلك الاستمرار.
مثال توضيحي:
- I was eating تعني "كنت آكل" أثناء فترة معينة إلى أن وقع حدث آخر.
- I had eaten تُظهر أن الأكل كان قد انتهى تمامًا قبل حدوث الحدث الآخر.
الفرق الرئيس هنا هو أن الماضي المستمر يُركّز على استمرارية الفعل في الماضي، بينما الماضي التام يُبرز اكتمال الفعل قبل لحظة زمنية أخرى.
متى أستخدم الماضي التام المستمر؟
يُستخدم الماضي التام المستمر عندما يكون الحدث قد استمر لفترة من الزمن في الماضي ثم انتهى قبل وقوع حدث آخر. صيغته الأساسية هي had been + الفعل بصيغة -ing.
على سبيل المثال:
- I had been eating تعني "كنت آكل لفترة ثم توقفت قبل أن يحدث شيء آخر".
يُفيد هذا الزمن في إبراز مدة الحدث السابقة للحدث الجديد، ما يجعله مزيجًا بين الاستمرارية والانتهاء قبل نقطة زمنية أخرى.
يُساعد ترتيب الأحداث وفهم سلسلة الزمن على التمييز بين استخدام قاعدة الماضي التام والماضي المستمر والماضي التام المستمر بسهولة ودقّة.
ما الكلمات الدالة على الماضي التام؟
الكلمات الدالة على قاعدة الماضي التام تساعد في تحديد ترتيب الأحداث بدقة في الزمن الماضي، فهي توضح أي حدث وقع أولًا وأيها تلاه. هذه الكلمات تعد إشارات زمنية مهمة لفهم المعنى الكامل للجملة.
- before (قبل): تُستخدم للإشارة إلى أن الحدث الأول وقع قبل حدث آخر.
مثال: They had left before I arrived.
(كانوا قد غادروا قبل أن أصل.)
- after (بعد): تدل على أن الحدث الثاني حدث لاحقًا للأول.
مثال: I went to bed after I had finished my homework.
(ذهبت إلى السرير بعد أن أنهيت واجبي.)
- already (سبق أن): توضح أن الفعل الأول اكتمل قبل وقت محدد في الماضي.
مثال: The movie had already started when I got there.
(كان الفيلم قد بدأ بالفعل عندما وصلت إلى هناك.)
- never (لم/أبدًا): تُستخدم لتعبر عن أن حدثًا ما لم يحدث حتى لحظة معينة في الماضي.
مثال: She had never seen the sea before that day.
(لم تكن قد رأت البحر قبل ذلك اليوم.)
- just (لتوّه): تشير إلى أن الفعل حدث قبل وقت قصير من حدث آخر في الماضي.
مثال: He had just left when you called.
(كان قد غادر لتوّه عندما اتصلتم.)
- when (عندما): تربط بين حدثين وقعا في الماضي وتوضح ترتيب وقوعهما.
مثال: I had finished eating when he arrived.
(كنت قد انتهيت من الأكل عندما وصل.)
- by the time (بحلول الوقت الذي...): تُظهر أن الفعل الأول كان قد اكتمل قبل النقطة الزمنية المشار إليها.
مثال: By the time we reached the station, the train had left.
(بحلول الوقت الذي وصلنا فيه إلى المحطة، كان القطار قد غادر.)
كيف أميز الجمل في الماضي التام؟
تمييز الجمل في قاعدة الماضي التام يعتمد على فهم ترتيب الأحداث في الزمن. الفعل الذي حدث أولاً في الماضي يُصاغ باستخدام had + التصريف الثالث للفعل، أما الفعل الذي جاء بعده فيُستخدم معه الماضي البسيط. بهذه الطريقة يمكنكم التعبير عن “حدث سابق لحدث ماضٍ آخر” بوضوح.
من المفيد استخدام خط زمني لتوضيح العلاقة بين الحدثين، مثلاً:
(حدث أول ➜ had + verb3) ← (حدث ثانٍ ➜ past simple).
يمكن تصور المخطط كخطٍّ أفقي يمثل الماضي، تُوضع عليه الأحداث بالترتيب حسب زمن وقوعها.
كيف أتعرف على الفعل الأسبق؟
لمعرفة أي فعل يجب صياغته في الماضي التام، يمكن الاستعانة ببعض المؤشرات اللغوية:
- وجود كلمات مثل before أو after يشير إلى تسلسل واضح بين حدثين.
- التعبير had already يدل على أن الفعل وقع قبل وقت أو حدث آخر.
- عند قراءة الجملة، فكروا: أي الفعلين حدث أولاً في الواقع؟ هذا هو الفعل الذي يُستخدم معه الماضي التام.
نصيحة: يمكنكم إعادة سرد الأحداث بترتيب زمني في أذهانكم أولاً، ثم إعادة صياغتها باستخدام القاعدة الصحيحة.
هل يمكن تقديم وتأخير ترتيب الجملة؟
نعم، يمكن في اللغة الإنجليزية تقديم أو تأخير ترتيب الجمل دون أن يتغير معنى الزمن، بشرط المحافظة على استخدام الماضي التام للفعل الأسبق.
على سبيل المثال:
- She had finished her homework before she went out.
- Before she went out, she had finished her homework.
في الحالتين، الحدث الذي تم أولاً هو الانتهاء من الفرض، لذا يُستخدم معه الماضي التام. ترتيب الجمل لا يؤثر على المعنى طالما تمّ الحفاظ على البنية الزمنية الصحيحة.
أمثلة متنوعة على قاعدة الماضي التام
تساعد الأمثلة على فهم قاعدة الماضي التام بطريقة أوضح، إذ تُظهر كيفية استخدام هذا الزمن في مواقف مختلفة للتعبير عن حدث وقع قبل حدث آخر في الماضي. في ما يلي أمثلة متنوعة توضح الجمل المثبتة والمنفية وكذلك الأسئلة واستخدام الكلمات الدالة على الماضي التام.
أمثلة على جمل مثبتة
يُستخدم الماضي التام في الجمل المثبتة للتعبير عن حدث اكتمل قبل وقوع حدث آخر في الماضي.
- She had left the room before the teacher arrived.
تُظهر هذه الجملة أن الفعل الأول وهو "مغادرتها الغرفة" حدث قبل وصول المعلم.
أمثلة على جمل منفية
عند النفي في قاعدة الماضي التام نضيف not بعد الفعل المساعد had للدلالة على أن الفعل لم يحدث قبل الحدث الآخر.
- He had not finished his work before he went out.
توضح الجملة أن الشخص خرج قبل أن يُنهي عمله، أي أن الحدث المتوقع لم يكتمل في الماضي.
أمثلة على الأسئلة
تُصاغ الأسئلة في الماضي التام من خلال تقديم الفعل المساعد had على الفاعل، ثم الفعل في صورته الثالثة.
- Had you ever visited Rome before last year?
يُستخدم هذا النوع من الأسئلة للسؤال عن خبرة أو تجربة سابقة قبل نقطة زمنية محددة في الماضي.
أمثلة مع الكلمات الدالة
تعزز الكلمات الدالة مثل just وalready وbefore المعنى الزمني في قاعدة الماضي التام، إذ تُظهر ترتيب الأحداث بوضوح.
- The train had just left when I reached the station.
في هذه الجملة تشير كلمة just إلى أن القطار غادر منذ لحظة قصيرة قبل وصول المتحدث إلى المحطة.
كيف أتقن قاعدة الماضي التام بسرعة؟
- مشاهدة فيديوهات مبسطة: تساعدكم المقاطع التعليمية القصيرة على فهم تكوين قاعدة الماضي التام واستخدامها الصحيح من خلال الأمثلة المرئية والنطق العملي.
- حل تدريبات عملية: كلما زادت التمارين التي تطبقونها، ترسخت القاعدة في أذهانكم، إذ تُظهر لكم الأخطاء المتكررة وتوضح الفروق الدقيقة في الأزمنة.
- تطبيق الأمثلة الواقعية: جربوا استخدام الماضي التام في مواقف يومية أو محادثات بسيطة لتصبح القاعدة جزءًا من تواصلكم الطبيعي.
- كتابة قصص قصيرة: عند كتابة قصة مشوقة مستخدمين فيها الماضي التام، تُجبرون على التفكير في ترتيب الأحداث زمنياً، مما يعزز استيعاب القاعدة.
- الاشتراك في دورات تفاعلية: الدورات عبر الإنترنت تمنح فرصة للتمرن المباشر وتلقي الملاحظات من مدرسين متخصصين بطريقة تشجع على التطور السريع.
ما منهجية أكاديمية انقلش بليس في تعليم قاعدة الماضي التام؟
تعتمد أكاديمية انقلش بليس على أسلوب مبسط يركّز على جعل قاعدة الماضي التام مفهومة من خلال الشرح العملي والتفاعل المباشر. يتم شرح القاعدة بخطوات واضحة، حيث يُوضَّح الفرق بين الأزمنة ويُبيَّن استخدام الماضي التام في سياقات الحياة اليومية، مما يساعد المتعلمين على إدراك المعنى الحقيقي خلف صيغة had + past participle.
ما شكل التدريبات العملية؟
تقدّم الأكاديمية مجموعة متنوعة من التدريبات التي تدمج بين الفهم والتطبيق العملي لقاعدة الماضي التام، وتشمل ما يلي:
- تمارين تحويل الجمل من المضارع التام أو الماضي البسيط إلى الماضي التام لضمان فهم تركيب الجمل بدقة.
- محادثات محاكية للواقع تُستخدم فيها القاعدة ضمن حوارات حياتية، مما يعزز استخدام اللغة بطلاقة وسياق طبيعي.
- اختبارات تقييمية دورية تقيس مدى استيعاب المتعلمين وتساعد في تحديد نقاط الضعف لتصويبها مبكرًا.
ما دور الدعم الفني والتفاعلي؟
توفّر أكاديمية انقلش بليس دعمًا فنيًا وتعليميًا متواصلًا عبر منصتها الرقمية، مما يتيح للمتعلمين التواصل بسهولة مع الفريق المختص عند مواجهة أي صعوبة. كما تنظم جلسات مراجعة مستمرة لمتابعة التقدم، وضمان إتقان قاعدة الماضي التام بمساعدة التفاعل المباشر.
الأسئلة الشائعة حول قاعدة الماضي التام
ما هي قاعدة الماضي التام؟
قاعدة الماضي التام تُستخدم للتعبير عن حدث وقع قبل حدث آخر في الماضي. تتكون الجملة من الفعل المساعد had متبوعًا بـ التصريف الثالث للفعل (past participle). يمكن تغيير ترتيب الأحداث في الجملة دون أن تتأثر القاعدة، طالما أن الحدث الأقدم يُصاغ بالماضي التام لتوضيح تسلسل الزمن بدقة.
ما هي قاعدة زمن الماضي التام؟
زمن الماضي التام يُبنى باستخدام الفعل المساعد had مع التصريف الثالث للفعل الرئيسي، ويُستخدم مع جميع الضمائر بنفس الصورة دون تغيير شكل had. يهدف هذا الزمن إلى ربط حدثين في الماضي وإبراز أن أحدهما سبق الآخر زمنًا.
كيف أعرف أن الجملة past perfect؟
يمكن معرفة أن الجملة في زمن الماضي التام إذا كانت تحتوي على حدثين في الماضي، وكان الأقدم منهما مصاغًا باستخدام had + التصريف الثالث للفعل. يُستخدم هذا الزمن لتوضيح التسلسل الزمني بين الأحداث.
الخلاصة
قاعدة الماضي التام تُعد من القواعد الجوهرية في اللغة الإنجليزية لأنها تمنحكم القدرة على ترتيب الأحداث بدقة زمنية واضحة، مما يجعل أسلوبكم في الكتابة والمحادثة أكثر احترافية وسلاسة. من خلال هذه القاعدة يمكنكم تحديد ما وقع أولاً وما تلاه، وهو ما يثري التواصل ويمنح اللغة بعدًا منطقيًا ومفهومًا.
اقرأ أيضًا:

تعليقات:
لا يوجد تعليقات
[[c.user.fullname]]
[[reply.user.fullname]]