قد يكون التحدث عن أحداث كانت جارية في الماضي مربكًا لعديدٍ من متعلمي اللغة الإنجليزية، خاصة عندما يحاولون وصف موقفين وقعا في الوقت نفسه أو حدثٍ قطع آخر. هنا تبرز أهمية قاعدة الماضي المستمر التي تمنح الجمل دقة ووضوحًا في الزمن وتساعد على ربط الأحداث بطريقة طبيعية ومنطقية.
في هذا المقال، ستتعرفون على كل ما تحتاجونه لفهم قاعدة الماضي المستمر بعمق: من شرح تركيبها واستخدامها الصحيح، إلى مقارنة تطبيقاتها مع الأزمنة الأخرى. كما ستتعلمون طرقًا عملية لتوظيفها في مواقف الحياة اليومية ونصائح خاصة من خبراء "أكاديمية انقلش بليس" في التعليم عن بعد، لتتمكنوا من تطوير مهاراتكم اللغوية بثقة وحيوية.
ما هي قاعدة الماضي المستمر؟
قاعدة الماضي المستمر تُستخدم للتعبير عن حدث كان جاريًا في فترة زمنية محددة في الماضي، أو كان يحدث أثناء وقوع حدث آخر. هذا الزمن يعطي إحساسًا بالاستمرارية والحدث الذي لم يكتمل بعد في تلك اللحظة الماضية، وكأنه يشكل خلفية لمشهد أو قصة تجري أحداثها في الماضي.
يُستعمل الماضي المستمر أيضًا مع أدوات الربط مثل when وwhile لبيان تزامن حدثين؛ فيُستخدم الماضي المستمر للفعل الأطول زمنًا، بينما يُستخدم الماضي البسيط للفعل الذي قاطعه أو حدث أثناءه. بهذا الأسلوب، يمكن رسم صورة زمنية دقيقة لوصف تسلسل الأحداث في الماضي بشكل مرن وواضح.
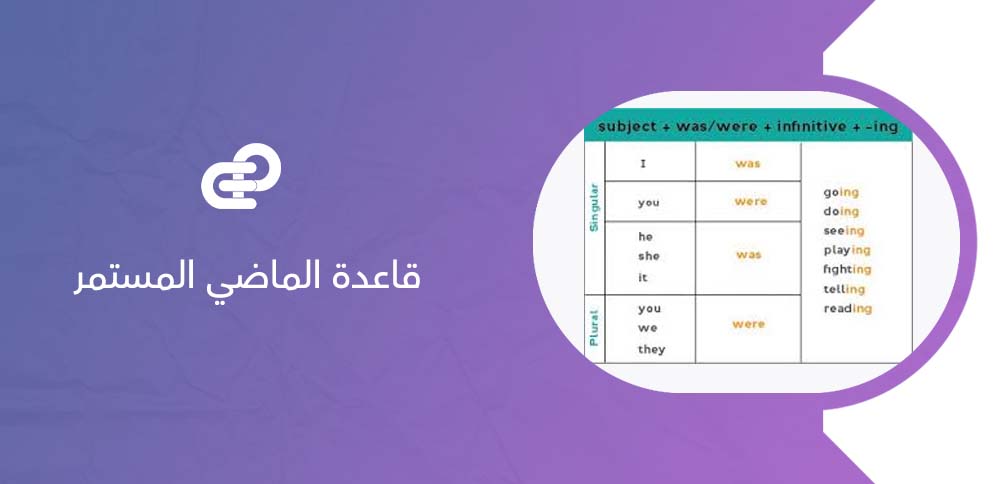
ما هي صيغة الماضي المستمر؟
- تتكوّن صيغة الماضي المستمر من الفاعل + was/were + الفعل مضافًا إليه ing، يلي ذلك بقية الجملة حسب المعنى المطلوب.
- يُستخدم was مع الضمائر I, he, she, it للدلالة على المفرد.
- تُستخدم were مع الضمائر we, you, they للدلالة على الجمع.
- مثال تركيبي يوضح القاعدة: Subject + was/were + verb-ing + (rest of sentence)، وهو النمط الذي يعبّر عن الفعل المستمر في الماضي بوضوح ودقة.
ما هي استخدامات قاعدة الماضي المستمر؟
يُستخدم زمن الماضي المستمر للتعبير عن أفعال كانت جارية في لحظة محددة في الماضي، وغالباً ما يربط بين حدثين وقعا في فترة زمنية واحدة، أو يصف سياقاً عاماً يهيئ القارئ أو السامع لفهم ما كان يحدث آنذاك.
كيف نستخدمه في المواقف اليومية؟
يمكن استخدام قاعدة الماضي المستمر في مواقف حياتية متكررة للتعبير عن أحداث لم تنتهِ وقت وقوعها، مثل:
- وصف نشاط كنتم تقومون به في وقت معين: At 6 pm yesterday, I was studying. أي "كنت أدرس في السادسة مساءً أمس".
- الحديث عن حدثين متزامنين: She was reading while he was cooking. أي "كانت تقرأ بينما هو يطبخ".
- توضيح موقف مستمر في الخلفية أثناء حدوث شيء آخر: The kids were playing outside all afternoon. أي "كان الأطفال يلعبون في الخارج طوال فترة الظهيرة".
يُفيد هذا الزمن في نقل صورة حيّة للحركة المستمرة في الماضي، مما يجعله شائعاً في الأحاديث اليومية والقصص الشخصية.
متى نستخدمه مع الماضي البسيط؟
يُدمج الماضي المستمر مع الماضي البسيط عندما نريد التعبير عن حدث مستمر انقطع فجأة بسبب وقوع حدث آخر. فالحدث المستمر يُصاغ بالماضي المستمر، بينما الحدث القاطع يُصاغ بالماضي البسيط. على سبيل المثال:
She was cooking when the phone rang. أي "كانت تطبخ عندما رن الهاتف".
هذا التركيب يوضح بدقة كيف كان أحد الأفعال جارياً في الماضي حتى تداخل معه حدث قصير أنهى استمراريته.
هل يصلح لسرد القصص؟
نعم، يُستخدم الماضي المستمر كثيراً في السرد القصصي، إذ يضفي عمقاً زمنياً على المشاهد ويُبرز الخلفية التي تقع فيها الأحداث. فمثلاً: It was raining heavily, people were running everywhere. هذا النوع من الجمل يرسم صورة حية لما كان يحدث في لحظة معينة، ويساعد على خلق أجواء مشحونة بالحركة والتفاصيل داخل القصة.
كيف نصيغ قاعدة الماضي المستمر؟
قاعدة الماضي المستمر بسيطة في تركيبها وتعتمد على الفاعل ثم فعل was أو were، يليه الفعل مضافًا إليه -ing، ثم بقية الجملة حسب المعنى المطلوب.
التركيب الأساسي يكون على الشكل التالي:
- Subject + was/were + verb-ing + (rest of the sentence)
أمثلة توضح القاعدة:
- She was watching TV when I called.
- They were playing outside.
- I was studying English yesterday evening.
اختيار was أو were يعتمد على الفاعل:
- نستخدم was مع (I, He, She, It).
- نستخدم were مع (You, We, They).
كيف نصيغ النفي؟
عند النفي في الماضي المستمر، نضيف كلمة not بعد was أو were، ويمكن أيضًا استخدام الصيغة المختصرة (wasn’t / weren’t) لتبدو الجملة أكثر طبيعية في الاستخدام اليومي.
مثال على ذلك:
- I was not studying.
- We were not sleeping last night.
- She wasn’t watching TV.
النفي هنا يشير إلى أن الفعل لم يكن جاريًا في لحظة معينة من الماضي.
كيف نكتب السؤال؟
لصياغة السؤال في قاعدة الماضي المستمر، نقدّم was أو were على الفاعل، ثم نكمل بالفعل المضاف إليه -ing وبقية الجملة.
بهذا الشكل:
- Was/Were + subject + verb-ing + (rest of sentence)?
أمثلة:
- Were you playing football?
- Was she reading when you arrived?
- Were they studying at that time?
هذا النوع من الأسئلة يساعد على الاستفسار عن حدث كان مستمرًا في الماضي.
أين نضع الكلمات الدالة؟
الكلمات الدالة مثل while وwhen تُستخدم كثيرًا مع قاعدة الماضي المستمر لربط الأحداث أو لتحديد لحظة وقوع الفعل المستمر مقارنةً بحدث آخر في الماضي.
عادةً ما تأتي هذه الكلمات في منتصف الجملة لربط حدثين متزامنين أو متتابعين، مثل:
- She was watching TV when I called.
- While they were playing, it started to rain.
- He was reading when the lights went out.
في التمارين التعليمية، يُفضَّل التركيز على مكان was/were والكلمة الدالة داخل الجملة لتثبيت القاعدة وفهم معناها الزمني بدقة.
ما هي الأمثلة المستخدمة على قاعدة الماضي المستمر؟
تُستخدم قاعدة الماضي المستمر للتعبير عن فعل كان مستمرًا في حدث معين في الماضي، وغالبًا ما يأتي معها وقت محدد أو حدث آخر يقطع الاستمرارية.
فيما يلي مجموعة من الأمثلة العملية التي توضّح تركيب واستخدام هذا الزمن خطوة بخطوة:
- I was eating dinner at 7 o’clock yesterday.
(كنت أتناول العشاء الساعة السابعة مساءً البارحة)
يُعبّر هذا المثال عن نشاطٍ استمر في وقت محدد من الماضي، وهو الساعة السابعة، مما يُظهر استمرارية الفعل خلال تلك اللحظة.
- She was watching TV when I called her.
(كانت تشاهد التلفاز عندما اتصلت بها)
يُستخدم هذا التركيب لبيان أن فعل المشاهدة كان جاريًا عندما حدث فعل آخر في الماضي، وهو الاتصال.
- We were studying English.
(كنا ندرس اللغة الإنجليزية)
مثال بسيط على استخدام الماضي المستمر لوصف فعل كان قائمًا في فترة ماضية دون التركيز على زمن بدايته أو نهايته.
- They were playing football.
(كانوا يلعبون كرة القدم)
يُظهر هذا المثال فعلًا جماعيًا كان جاريًا في الماضي، مما يُبرز الاستمرارية ضمن سياق زمني محدد.
- Was he playing football?
(هل كان يلعب كرة القدم؟)
مثال على صيغة السؤال في الماضي المستمر، حيث نبدأ بـ was قبل الفاعل، مما يوضّح طريقة تحويل الجملة إلى سؤال.
- I was not (wasn’t) sleeping.
(أنا لم أكن نائمًا)
يوضح هذا المثال الشكل المنفي للزمن الماضي المستمر باستخدام was not أو اختصارها wasn’t.
يساعد التدريب على أمثلة مشابهة في فهم الفرق بين الماضي المستمر وبقية الأزمنة كالـماضي البسيط، كما يُنمي لدى المتعلّمين مهارة التحدّث والكتابة بشكلٍ أكثر دقة وطبيعية.
يُنصح المتعلّمون العرب بتكوين جمل جديدة على هذا النمط لتجنّب الأخطاء الشائعة في ترتيب الأفعال أو استخدام was وwere.
ما هي تحديات ودروس تعلم قاعدة الماضي المستمر؟
يتكرر وقوع المتعلمين في مجموعة من الأخطاء أثناء استخدام قاعدة الماضي المستمر، وغالبًا ما ترتبط هذه الأخطاء إما بصياغة الفعل أو بترتيب الجملة. من أبرزها:
- نسيان إضافة ing إلى الفعل الرئيس، ما يجعل الجملة ناقصة المعنى وغير صحيحة نحويًا.
- استخدام was وwere بشكل خاطئ مع الفاعل، كأن يُستعمل "was" مع الجمع أو "were" مع المفرد.
- وضع الكلمات الدالة مثل while أو when في غير موضعها الصحيح داخل الجملة، مما يغير المعنى الزمني المقصود.
- الخلط بين الماضي البسيط والماضي المستمر عند سرد أحداث متداخلة؛ كالتعبير عن حدثين وقعا في وقت واحد بطريقة لا توضح الحدث المستمر مقابل الحدث المفاجئ.
كيف أتفوق في قاعدة الماضي المستمر؟
للتفوق في إتقان قاعدة الماضي المستمر، من المفيد التعامل معها كتسلسل من الممارسة والفهم التدريجي. فأنتم بحاجة إلى بناء تصور واضح عن زمن الحدث المستمر ثم الانتقال إلى التطبيق العملي. ينصح بما يلي:
- ممارسة كتابة الجمل يوميًا باستخدام الزمن بشكل طبيعي في مواقف الحياة اليومية.
- مراجعة تركيب الجمل بصوت مرتفع لتثبيت النطق الصحيح والإيقاع الزمني.
- تدوين أبرز الملاحظات حول استخدام was/were في دفتر خاص بالقواعد لتجنب التكرار في الخطأ.
- البحث عن أنشطة تفاعلية أو اختبارات قصيرة تساعدكم على ترسيخ الاستخدام الصحيح للزمن.
ما هي أفضل الاستراتيجيات لتعلم الماضي المستمر؟
لكي يصبح تعلم قاعدة الماضي المستمر ممتعًا وسهلًا، يمكن اتباع مجموعة من الاستراتيجيات العملية التي أثبتت فعاليتها:
- تدريج الشرح: البدء بالأمثلة البسيطة ثم الانتقال تدريجيًا إلى الجمل المركبة يتيح استيعاب البنية اللغوية بوضوح.
- توظيف التمارين العملية: تطبيق القاعدة من خلال الكتابة أو المحادثة يعزز الفهم أكثر من الاكتفاء بالحفظ النظري.
- ربط الدروس بمواقف واقعية: استخدام حوارات قصيرة أو مواقف يومية يساهم في ترسيخ الزمن في الذاكرة طويلة المدى.
- الأمثلة التوضيحية والوسائط البصرية: عرض الجمل مع صور أو مقاطع فيديو يجعل القاعدة أكثر وضوحًا وسهولة في التذكر.
- استخدام المنصات التفاعلية مثل أكاديمية انقلش بليس، حيث يمكن متابعة دروس مباشرة واختبارات قصيرة بعد كل وحدة.
- تكرار التطبيق والنقاش: في كل مستوى من التعلم، يجب تكرار بناء الجمل ومناقشتها شفهيًا مع الزملاء أو المعلم لتصحيح الأخطاء في السياق الفعلي.
كيف تساعد المنصات التعليمية في إتقان قاعدة الماضي المستمر؟
تُعد الدروس التفاعلية من أكثر الوسائل فعالية في تعلم قاعدة الماضي المستمر، لأنها تمنح المتعلمين فرصة المشاركة الحقيقية في عملية التعلم. فبدلاً من الاكتفاء بالاستماع أو القراءة، يتفاعلون مباشرة مع المدرّسين والأنشطة، مما يعزز الفهم ويثبّت القواعد في الذاكرة. كما أن التصحيح الفوري للأخطاء يساعد على معالجة نقاط الضعف فور ظهورها، ويمنح الطلاب ثقة أكبر في استخدام الأزمنة بشكل صحيح داخل الجمل والمحادثات.
كيف تقدم أكاديمية انقلش بليس هذا الدرس؟
أكاديمية انقلش بليس، وهي منصة تعليمية رائدة في تعليم اللغة الإنجليزية عن بعد منذ عام 2009، تركز على تقديم تجربة تعلم متكاملة ومتوازنة. تقدم الأكاديمية محتوى غني ومبتكر يهدف إلى ترسيخ فهم قاعدة الماضي المستمر وتعزيز مهارات استخدام الزمن في المحادثة والكتابة.
- توفر الأكاديمية دروسًا مباشرة وأخرى مسجلة تناسب مختلف المستويات، من المبتدئين إلى المتقدمين.
- تغطي دروسها مجالات القواعد، المحادثة، القراءة، الكتابة، والمفردات بطريقة متكاملة.
- تتيح بيئة تعليمية تفاعلية تعتمد على التطبيق العملي والتدريب المستمر.
- تقدم مصادر مرئية وسمعية تدعم الفهم، وجلسات افتراضية للنقاش والتدريب على المحادثة الواقعية.
- توفر تمارين دعم إضافية واختبارات دورية لقياس التقدم وضمان التطبيق العملي لما يتم تعلمه.
بهذا الأسلوب، تتحول دراسة قاعدة الماضي المستمر إلى تجربة تطبيقية وليست مجرد حفظ لقواعد لغوية.
ما الاستراتيجيات الفعالة للتعلم عن بعد؟
تتبنى الأكاديمية مجموعة من الاستراتيجيات التي أثبتت نجاحها في تعليم قواعد اللغة الإنجليزية، بما في ذلك قاعدة الماضي المستمر:
- التدرج في الشرح: يبدأ الدرس من المفاهيم الأساسية ثم يتوسع تدريجيًا نحو الاستخدامات الأكثر تعقيدًا.
- الدروس المباشرة: تسهم اللقاءات الفورية مع المعلمين في تعزيز التواصل وفهم التفاصيل الدقيقة.
- تقسيم المحتوى حسب المستوى: يضمن أن يتعلم كل طالب وفق قدرته وسرعته في الاستيعاب.
- التصحيح الفوري للأخطاء: يمنع تراكم الأخطاء اللغوية ويعزز الثقة في استخدام القواعد.
- التمارين العملية والمتابعات المستمرة: تساعد على ترسيخ المهارة من خلال التطبيق الواقعي للنظريات.
هذه الاستراتيجيات تخلق بيئة تعليمية متكاملة تتيح لكم تعلم القواعد بعمق واستفادة طويلة الأمد.
الأسئلة الشائعة حول قاعدة الماضي المستمر
ما هي قاعدة زمن الماضي المستمر؟
قاعدة الماضي المستمر تُستخدم لوصف حدث كان جاريًا في وقت محدد من الماضي، وغالبًا ما يرافقها ذكر هذا الوقت. الصيغة الأساسية هي: Subject + was/were + verb-ing، أي أن الفعل يُضاف إليه -ing بعد الفعل المساعد was أو were حسب الفاعل. هذا الزمن يُستخدم عندما نرغب في التعبير عن موقف مستمر في الماضي وليس فعلاً حدث وانتهى.
ما هي قاعدة when في الماضي المستمر؟
قاعدة when في الماضي المستمر تُستخدم عندما يكون هناك حدثان في الماضي؛ أحدهما كان مستمرًا والآخر قاطعه فجأة. الحدث المستمر يكون بصيغة الماضي المستمر، بينما الحدث الذي قطعه يُكتب بالماضي البسيط.
كيف أعرف أن الجملة past continuous؟
يُعرف زمن الماضي المستمر من خلال وجود was أو were متبوعة بالفعل بصيغة verb-ing، وغالبًا يظهر معه ظرف زمني يشير إلى مدة أو نقطة زمنية في الماضي. المقارنة بين الجمل توضح الفرق بوضوح: I played basketball yesterday → استخدم الماضي البسيط للتعبير عن فعل حدث وانتهى، I was playing basketball at 5 p.m. → استخدم الماضي المستمر للدلالة على أن الفعل كان جاريًا في وقت محدد بالماضي.
الخلاصة
قاعدة الماضي المستمر تُعد من الركائز الأساسية في تعلم اللغة الإنجليزية، إذ تتيح التعبير عن الأحداث التي كانت جارية في لحظة محددة من الماضي. استخدامها يمنح اللغة سلاسة في السرد، ويُظهر الترابط الزمني بين الأفعال بطريقة طبيعية تُثري أسلوب المتحدث أو الكاتب.
اقرأ أيضًا:

تعليقات:
لا يوجد تعليقات
[[c.user.fullname]]
[[reply.user.fullname]]